Amidst the many natural wonders of a state like New Mexico, it can be easy to overlook local gems like Carlito Springs. Located just 20 minutes east of downtown Albuquerque, Carlito Springs feels more like the Appalachian Mountains than the southwest. It’s a place with quirky New Mexico history, lush foliage, and inspiring landscaping.

The History
Carlito Springs was first settled in 1882 by Civil War veteran Horace Whitcomb while he looked for gold. In 1930, it was bought by Carl Magee, editor of the Albuquerque Tribune and patent-holder for the parking meter. He named it “Carlito” for his son, Carl Jr., who died in a plane crash. (This link contains an excellent and more detailed history.)
Of course tuberculosis, America’s deadliest disease at the time, played a role in Carlito’s history. In 1910, 3000 of Albuquerque’s 13,000 residents were people seeking treatment in the dry, high air. Today, Lovelace and Presbyterian Hospitals, two of the largest systems in the city, remain from the tuberculosis treatment days. Magee’s wife was tubercular. The property was used as a sanitorium before Magee’s purchase.
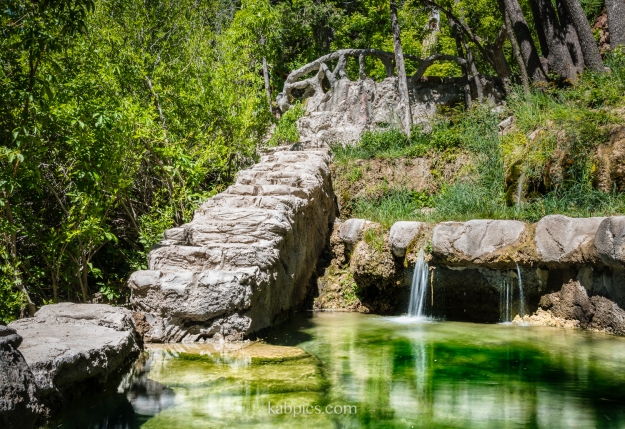
Magee’s daughter married a Sandia atomic scientist, and many of the features of the property date from that time. The pair won many ribbons at the New Mexico State Fair as “master gardeners,” and planted flowers and fruit trees on the property. Today, architect Baker Morrow calls Carlito springs “one of the most amazing landscapes in the southwest.” The property has several cabins, as well as the springs, several highly manicured fishing pools (no longer stocked), fruit trees and flowers. If you’re an engineering nerd like me, you can check out the rusty vintage concrete pourer, which I suppose was used to craft the lovely railings around the ponds.
Carlito Springs was only permanently opened to the public in August of 2014. Because the property is on the steep banks of Tijeras canyon, substantial work went into building the trails that lead to this historic property. They did a great job, and Carlito Springs is a great Albuquerque attraction.
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
The Hike
The hiking loop is about 2.4 miles, with about 400 feet of elevation change. From the parking lot, take the fork left for the most direct route to the cabins and ponds. This is the steepest section of the loop; it follows the springs up the side of the canyon, but it is cool and shady. The trails is good quality, without many rocks or roots to impede footing. The last few hundred feet before the cabins are switchbacks.
On the first leg of the hike, mind the poison ivy which grows near the trail. In May, there was quite a bit of it, neon green and inviting, but the trail is wide enough that it’s easy to avoid. By the cabins and on the second part of the loop, I didn’t see any.
To the left of the cabins (if you are facing them), you can follow a small spur which leads to a view of the valley. It’s a steep walk and you get the view later anyways; when I do the hike again I will skip this spur.
To the right of the cabins (again, as you face them) the loop continues. Just past the largest building, you will find the cement mixer, some various old rusted implements, and a port-o-potty. By the cement mixer, you can look into Tijeras Canyon, this time without the extra vertical effort. It’s a pretty enough view, besides the mining facility (which I omitted from my image).
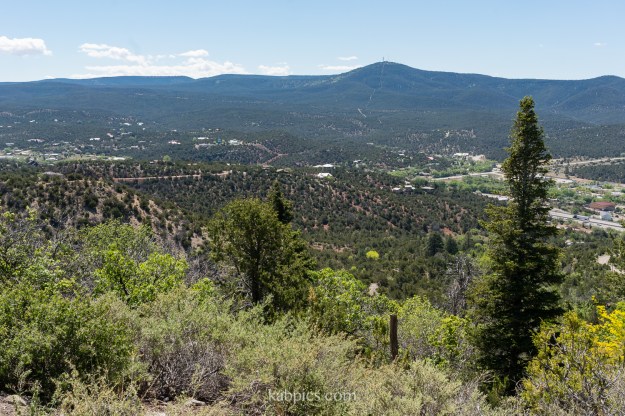

The final leg of the loop is sunny and gently sloping. Here, you see red soil and cacti rather than water and poison ivy. In May, the sun was pleasant, but this south-facing trail could be hot later in summer. We had this portion of the trail to ourselves.
May was a great time for this hike. Up by the cabins, peonies and columbines bloomed. Later in the hike, cacti bloomed. We read about wildlife sightings such as bears and deer at Carlito, but on a busy Saturday, we had no encounters.
Extras
Carlito Springs is only a couple of miles from the famous “singing road” portion of Route 66. You can take Route 66 (Central Ave) from Albuquerque, or you can overshoot the Carlito Springs turn and u-turn. The singing portion is only eastbound. It’s silly, but entertaining.

















,_Santa_Fe,_New_Mexico.jpg)